As residents of New England, we may not face hurricanes as frequently as our counterparts in the southern U.S., but the impact of intense storms, floods, and coastal surges is not foreign to us. In light of the devastation caused by hurricanes like Harvey, Irma, and Maria, it's crucial for homeowners in our region to also consider the role of insulation in post-hurricane home repair.
Here we’d like to explore the challenges posed by flooding and storm surges, the shortcomings of traditional insulation, and why closed-cell spray foam insulation, a FEMA-recognized flood-resistant material, emerges as a resilient solution.
Understanding the Impact of Hurricanes in New England
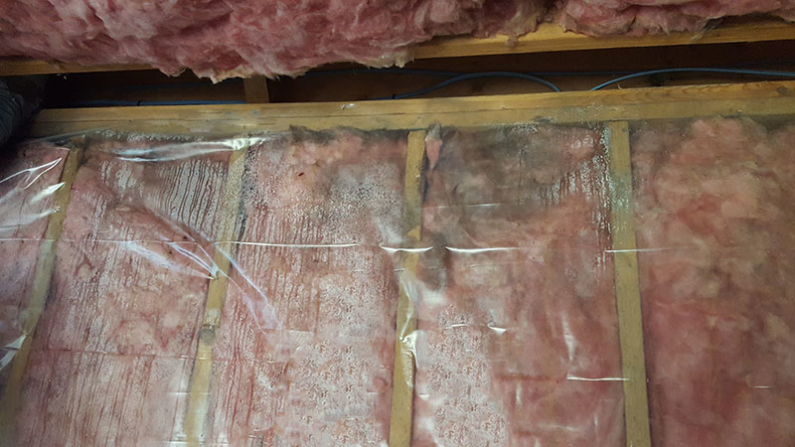
While New England is not a hurricane hotspot, we've witnessed the aftermath of intense storms that bring heavy rain, flooding, and potential storm surges along the East Coast. Coastal flooding poses a significant threat to homes, leading to physical deterioration, mold growth, and a host of other issues. According to FEMA, flooding is a major contributor to over $3.5 billion in insurance claims annually, and the risks associated with storm surges and underperforming drainage systems are ever-present.
The Pitfalls of Traditional Insulation
Traditional insulation materials, such as fiberglass and cellulose, excel at insulating homes from seasonal temperature variations but offer little protection against flooding. When floodwaters infiltrate a home, these materials become laden with moisture, rendering them unable to dry out quickly enough to prevent damage. Mold growth becomes a significant concern, posing health risks and complicating the post-hurricane cleanup process. Recognizing these limitations, FEMA emphasizes the importance of flood-resistant building materials in the reconstruction or repair of hurricane-impacted structures.
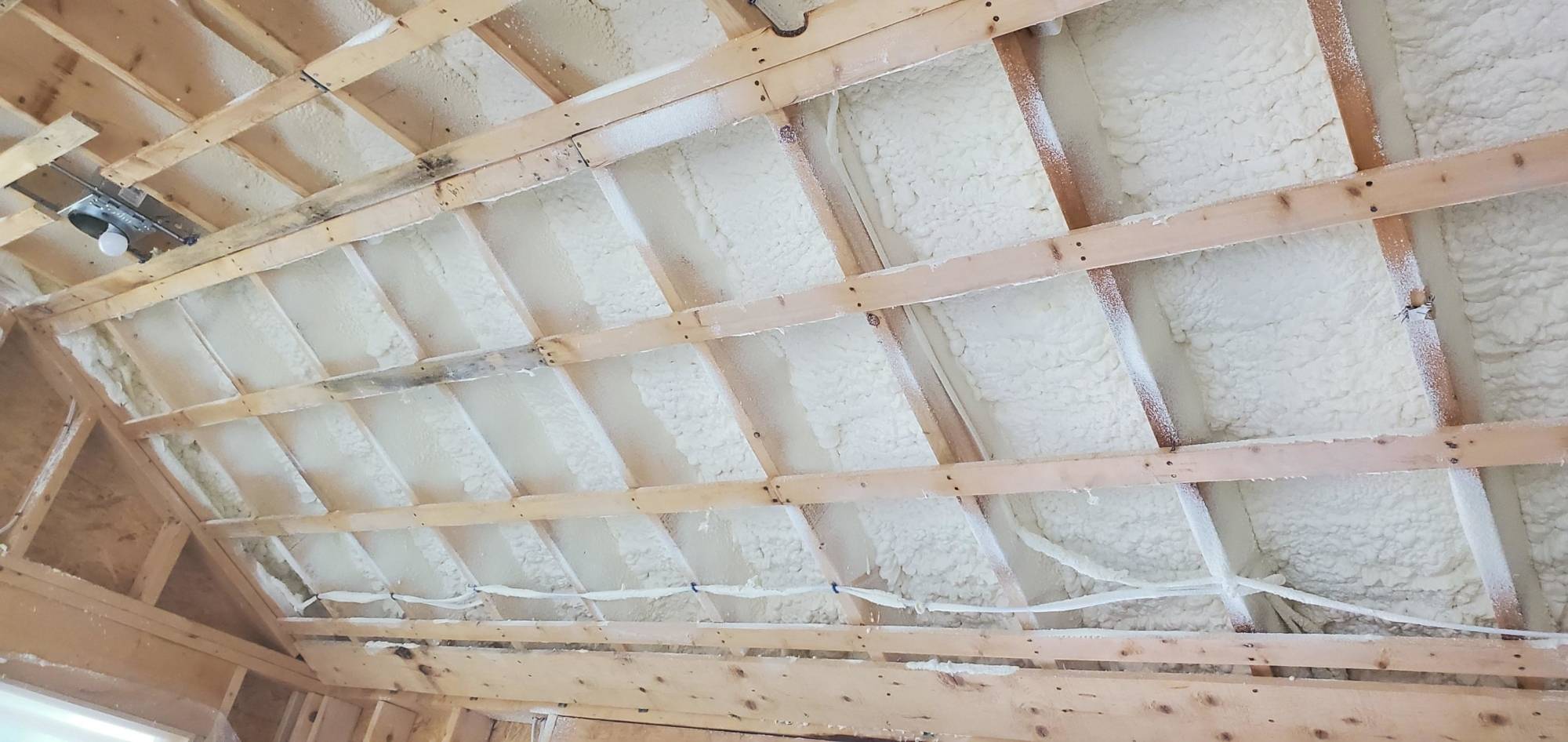
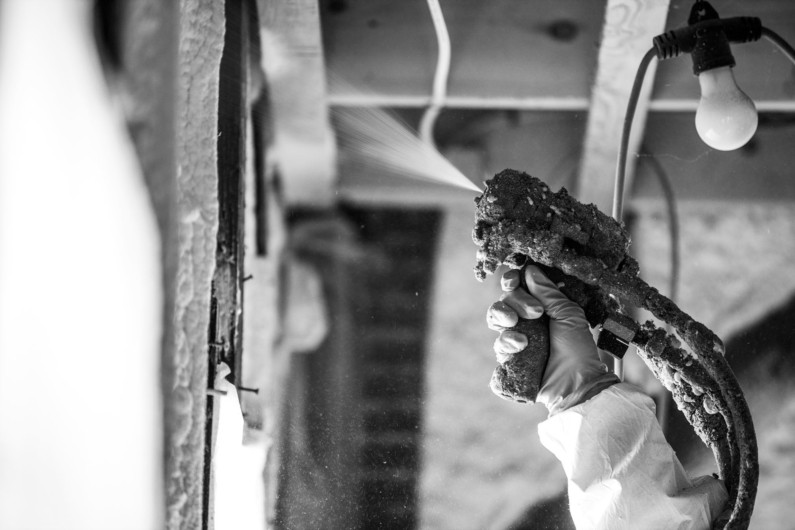
Closed-Cell Spray Foam: A Flood-Resistant Solution
FEMA identifies closed-cell spray foam insulation as a flood-resistant material falling into Class 4 or Class 5 of its flood damage-resistance classification system. Unlike traditional insulation, closed-cell spray foam quickly becomes rigid, adding structural integrity to roofs and reducing the risk of blowoff during hurricanes. This resilience makes it a valuable asset for homes in areas prone to flooding, hurricanes and heavy storms (like any nor’easter for example) J
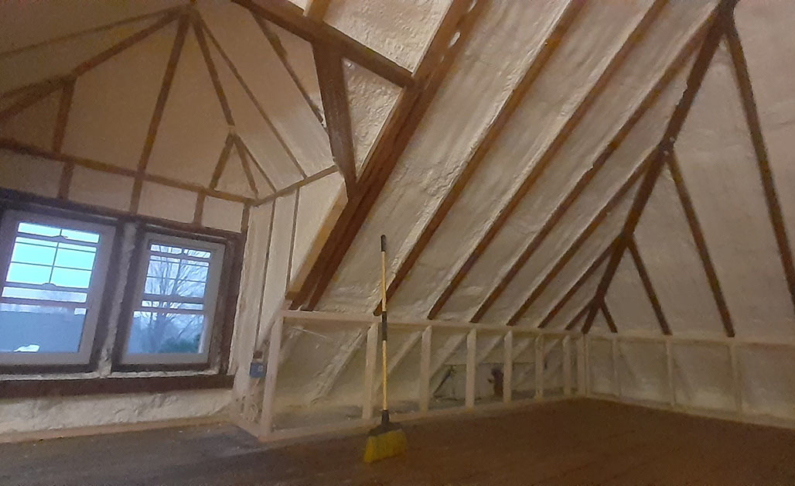
Key Features of Closed-Cell Spray Foam Insulation
- Structural Integrity: Closed-cell spray foam insulation, like that available from Icynene, enhances a home's structural integrity. This feature becomes crucial during hurricanes, where the rigidity of the insulation helps fortify roofs against the forces of strong winds.
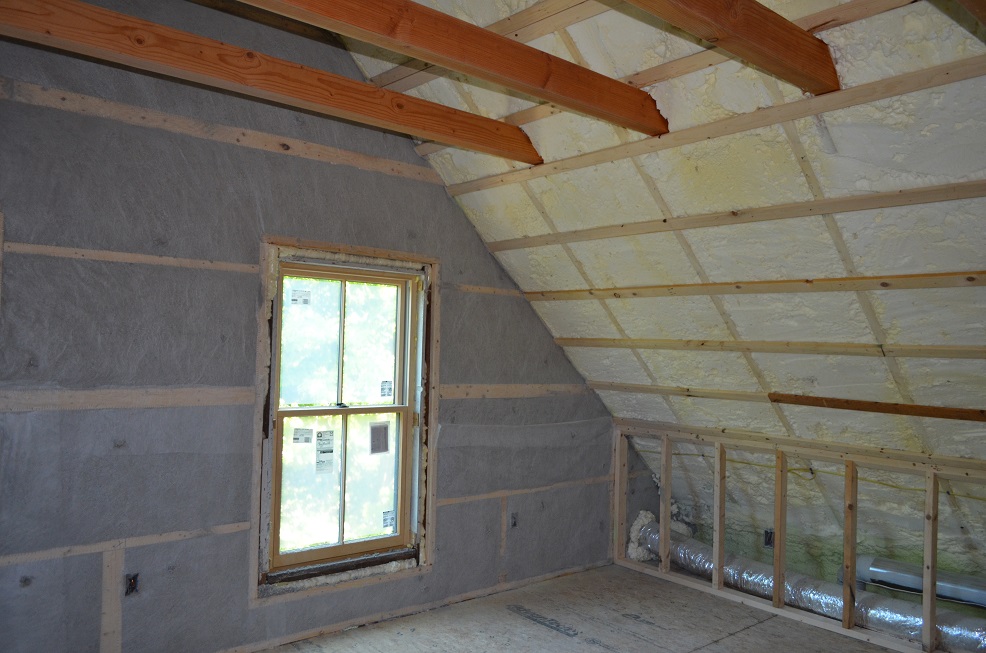
- Bulk Water Ingress Resistance: Closed-cell spray foam's ability to reject bulk water ingress is a game-changer in flood-prone areas. Applied in spaces like basements or crawlspaces, it helps reduce the risk of significant damage caused by hurricanes, storms, and their associated floodwaters.
- Air-Sealing Qualities: Beyond flood resistance, closed-cell spray foam insulation's air-sealing qualities contribute to long-term benefits. Homeowners can potentially reduce the size of their heating and cooling equipment, leading to energy savings and enhanced comfort throughout the year.
Preparing for the Future: A Resilient Home with Closed-Cell Spray Foam
As we've witnessed an increase in the intensity of hurricanes and heavy storms over the past 30 years, the importance of resilient home construction cannot be overstated. Having a home insulated with closed-cell spray foam insulation is an effective strategy to ensure preparedness for the next hurricane season. By leveraging its flood-resistant properties, structural benefits, and energy efficiency, homeowners can fortify their homes against the challenges posed by intense storms.
In the face of unpredictable weather patterns and the increasing intensity of hurricanes, New England homeowners must prioritize resilience in home construction and repair. Closed-cell spray foam insulation emerges as a FEMA-recognized flood-resistant solution, offering structural integrity, water ingress resistance, and long-term energy efficiency. As we navigate the complexities of our region's climate, investing in closed-cell spray foam insulation becomes a proactive step towards fortifying our homes and ensuring the well-being of our families in the aftermath of intense storms and flooding.