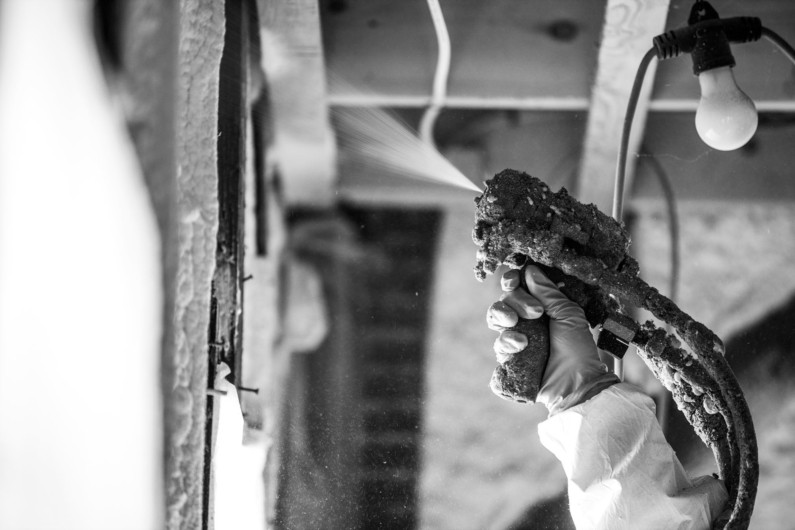
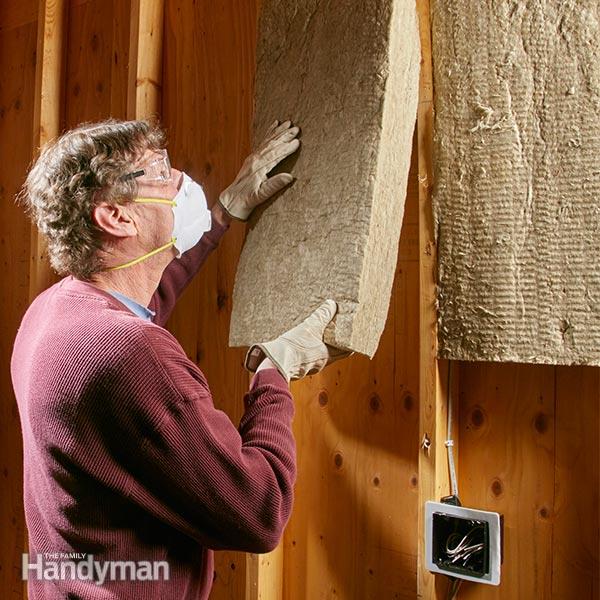
Incorrectly installed basement insulation is a common error. We see this problem not only with do-it-yourself installation, but also with contractor installation. The results can be disastrous as severe mold and mildew may become a problem, not to mention the loss of money on your heating bill. This is why we beg you, “don’t make these basement insulation mistakes.”
Use Treated Lumber
Since most basements are inherently moist, you need to keep all untreated wood away from the concrete surfaces. Moisture below the slab can wick up into the concrete and get to the base plates of the wall. Therefore, you need to make certain the bottom plate of the wall is treated lumber.
Avoid Using Fiberglass Insulation in Basements
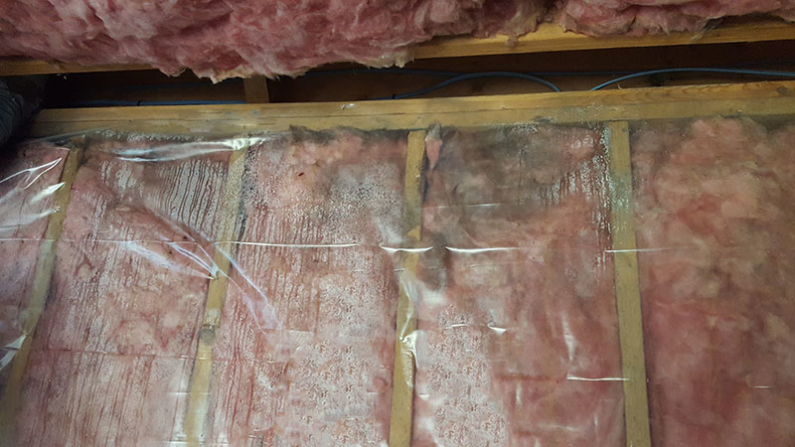
As seen in the photo above, putting polyethylene over fiberglass insulation is a no-no as it doesn’t allow the insulation to breathe. Consequently, this homeowner had moisture build-up and ultimately mold growth!
For years contractors have been treating basements much like regular living space. It’s not uncommon to see fiberglass insulation in direct contact with basement foundation walls. Here in the northeast, we see several common mistakes, including:
- Plastic vapor barrier against concrete wall, fiberglass insulation inside stud wall, then drywall
- Fiberglass insulation inside a “bag” hanging from the rim joist down along the foundation wall
- Stud wall filled with fiberglass insulation an inch or two away from the concrete wall[1]
Those mistakes can increase the chances for mold to grow.
What Causes Mold to Grow in Basements?

Mold can grow on virtually any organic material as long as it has the right moisture level and oxygen. Because mold eats or digests what it is growing on, it can damage a building and its furnishings. If left unchecked, mold eventually can cause structural damage to building materials and can cause health problems. That’s why we don’t want mold in our basements! Specifically, we can prevent damage to buildings and building contents in the basement areas, save money, and avoid these potential health problems by controlling moisture.
According to the EPA, indoor relative humidity in homes should be kept below 60 percent — ideally between 30 and 50 percent. [2] In addition to preventing mold formation, maintaining the correct humidity levels may also have a bonus effect. It may discourage pests such as cockroaches, silverfish (bristletails), and dust mites from showing up where you don’t want them!
To measure the humidity of your home or basement, you need to buy a humidity meter and track the relative humidity level. That is the first part of understanding the mold problem in your home or basement.
Education Needed
If contractors are still using fiberglass insulation in basements, it means that we in the industry need to do a better job educating our builders. In order to understand the issues with basement insulation, you first must understand the role of vapor barriers in basements.
Use the Right Insulation
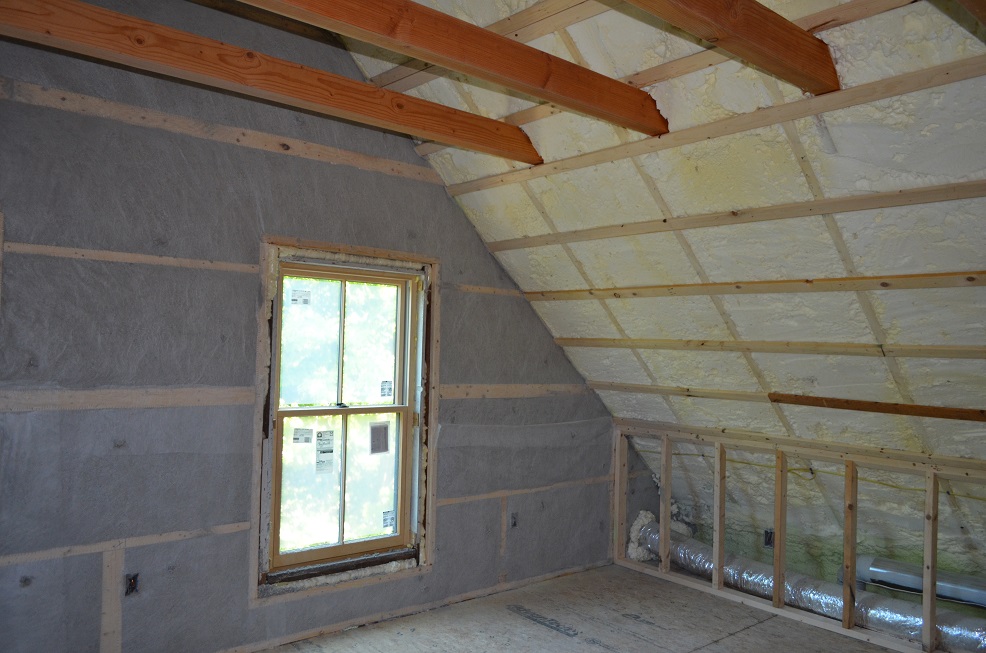
Over the years, we’ve come to rely on two main approaches for basement insulation projects and remodeling, including closed cell spray foam and rigid foam board. When installed in the correct thickness, these two methods result in a proper vapor barrier and superior insulation.
Insulating basements can be hard. They add a lot of space to a house, but they also have their own problems with temperature and moisture that make it hard to put in insulation. If you use the wrong materials or don’t think about important environmental factors, you could end up with mold, heat loss, and costly repairs in the future. It’s just as important to know what not to do as it is to know what to do when upgrading your home.
Why Traditional Insulation Methods Fail in Basements
Most people think that the same insulation that works in attics and walls will also work in basements. Unfortunately, everyday things like blown-in cellulose and fiberglass batts aren’t good for use in certain areas. Basements will soak up water from the soil around them and change in humidity, which is the perfect environment for these kinds of materials to lose their strength.
That’s where things like closed-cell spray foam insulation come in. Fiberglass makes a barrier that is not continuous for moisture and air but closed-cell spray foam makes a barrier that is continuous and fills in gaps to stop condensation from forming behind the walls. Not only does professional spray foam insulation keep the building warm, it also protects it from long-term water damage.
How to Monitor and Control Basement Humidity
If you don’t control the humidity in the basement, better insulation won’t help. Too much humidity lowers the R-value of insulation, causes wood framing to expand, and encourages mold growth. First, use a good hygrometer to keep an eye on the humidity levels and check the readings often. It is important to keep the humidity in the basement between 30% and 50%.
If your readings are too high, you can use a good dehumidifier to control the air. Also, it’s important to have good airflow. To Prevent areas of stagnant, damp air. Before putting in insulation, fix any signs of water getting in, like cracks in the foundation or windows that leak.
These moisture management steps, when used with closed-cell spray foam insulation, create a double layer of protection that keeps water out and keeps the inside of the house warm. This is great for homeowners who want to insulate their homes and need something that will last and save energy in the long run.
Get Educated – Be the Pro!
Today, the building industry and building science are changing rapidly. In order to stand out in the competition and provide a professional service to your clients, you need to stay educated on the latest methods. You can be sure that the team at The Green Cocoon is up-to-date on the latest insulation practices in order to bring our clients the best product possible.
If you have questions or need a quote on your next insulation project, contact us and we’d be happy to help.
[1] Be the Pro. Avoiding Basement Insulation Mistakes. Retrieved from bethepro.com.
[2] United States Environmental Protection Agency. Mold Course Chapter 2. Retrieved from epa.gov.
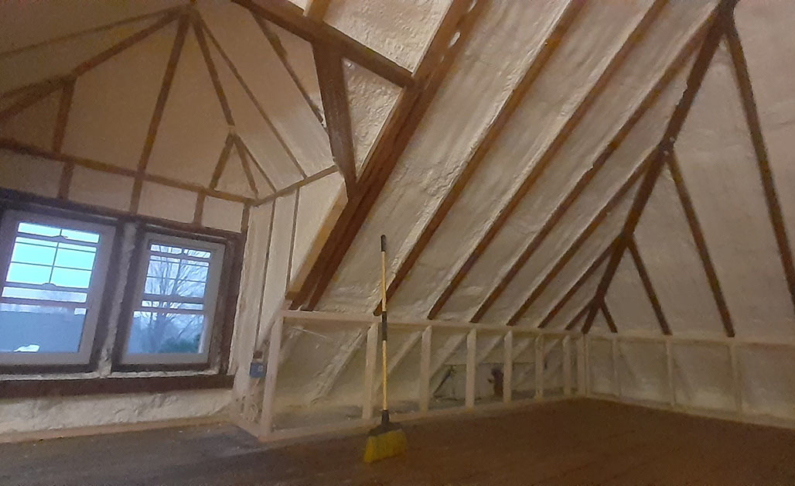










 Now let’s take the square footage (864 feet) times the overall height (25 feet) and you’ve got 21,600 cubic feet. When multiplied by 40 ACH, you will have to move 864,000 cubic feet of air in an hour!
Now let’s take the square footage (864 feet) times the overall height (25 feet) and you’ve got 21,600 cubic feet. When multiplied by 40 ACH, you will have to move 864,000 cubic feet of air in an hour!



 You must use the correct material for the environment, especially in cold temperatures. According to
You must use the correct material for the environment, especially in cold temperatures. According to  Proper storage of both the applicator and the spray foam is critical for a successful application during cold weather conditions. Both components must be at a minimum of 70°F to ensure that the supply pumps can move the material to the spray machine at an appropriate rate.
Proper storage of both the applicator and the spray foam is critical for a successful application during cold weather conditions. Both components must be at a minimum of 70°F to ensure that the supply pumps can move the material to the spray machine at an appropriate rate.

